Template Strand Definition
Template Strand Definition - The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Web each strand then serves as a template for a new complementary strand to be created. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. The strand of the template dna double helix that is oriented so that the replication fork. The primary enzyme involved in this is dna polymerase which joins nucleotides to synthesize the. A particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated; One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The strand of the template dna double helix that is. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. The dna strand that would correspond to the mrna is called the coding or sense strand. The strand of the template dna double helix that is oriented so that the replication fork. Web each strand then serves. Web each strand then serves as a template for a new complementary strand to be created. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. The template strand. Web the template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. The template strand of the dna double helix that is oriented so that the replication fork moves along it in the 3′ to 5′ direction; Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. The dna strand that would correspond to the mrna is called the coding or sense strand. It is complementary to the coding strand of dna for the target gene. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Web each strand then serves as a template for a new complementary strand to be created. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. A particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated; The primary enzyme involved in this is dna polymerase which joins nucleotides to synthesize the. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript.
What Is The Template Strand

Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Definition
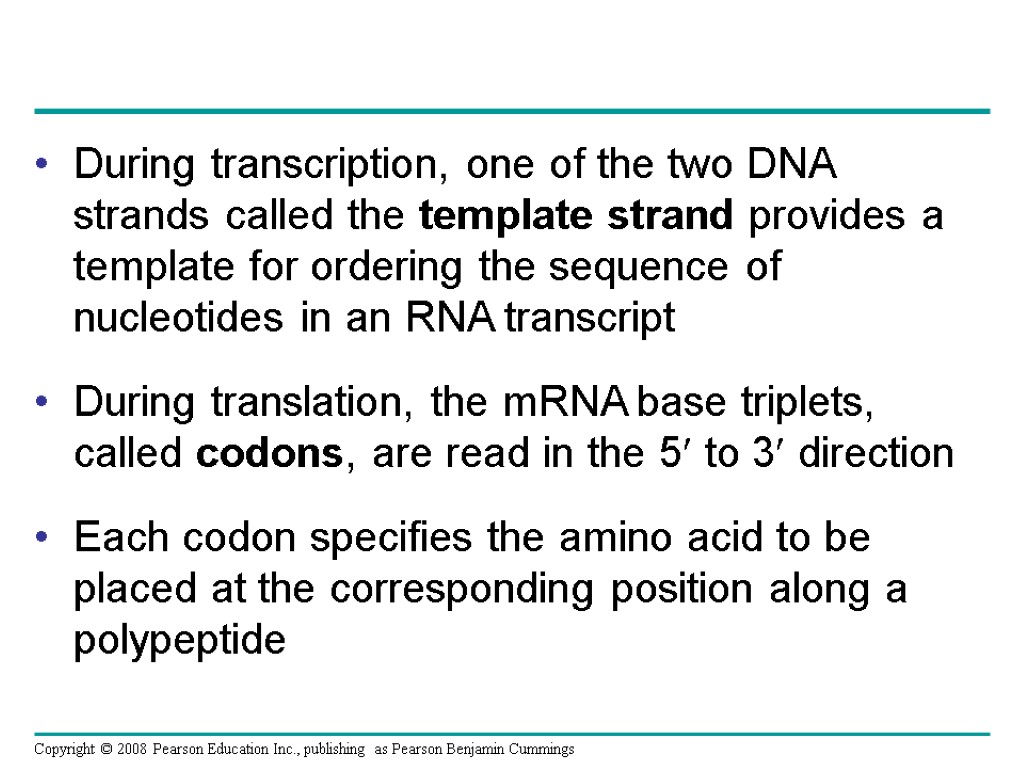
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein. Overview The
The Other Strand, The Coding Strand, Is Identical To The Rna Transcript In Sequence, Except That It Has Uracil (U) Bases In Place Of Thymine (T) Bases.
Web During Dna Replication, Each Of The Two Strands That Make Up The Double Helix Serves As A Template From Which New Strands Are Copied.
Web In Most Organisms, The Strand Of Dna That Serves As The Template For One Gene May Be The Nontemplate Strand For Other Genes Within The Same Chromosome.
The Strand Of The Template Dna Double Helix That Is Oriented So That The Replication Fork.
Related Post: